In a recent webinar hosted by Dan Kara from The Robot Report, an insightful overview of the integration of machine learning (ML) and generative AI in the field of robotics was presented. The session highlighted various platforms and technologies from major cloud service providers and innovative companies, showcasing how they are revolutionizing the robotics landscape.

AWS Cloud Services
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is at the forefront of providing cloud-based solutions for robotics through its AWS RoboMaker platform. This platform facilitates the development of internet-connected robots by offering seamless integration with other AWS services. One of its standout features is the support for the Robot Operating System (ROS), which is further enhanced by AWS’s cloud extensions for ROS, enabling developers to leverage the cloud for advanced machine learning applications. In addition, AWS RoboMaker includes a powerful robot simulator, Gazebo, which aids in the testing and development of robotic systems. Other AWS tools like TensorFlow and PyTorch are integral to developing machine learning models on this platform.
Google Cloud Robotics Platform
Google’s approach to robotics is deeply embedded in its cloud infrastructure. The Google Cloud AI Platform provides extensions for TensorFlow and AutoML, making it easier for developers to integrate AI into their robotic systems. Google Cloud’s data storage and analytics services also offer robust support for handling the vast amounts of data generated by robots, which is crucial for training and refining machine learning models.
Microsoft Azure Robotics
Microsoft’s Azure Robotics integrates machine learning and cognitive services directly into robotics development. Similar to AWS, Azure also supports Gazebo for simulation. Azure’s strength lies in its comprehensive AI and machine learning offerings, which are seamlessly integrated into the robotics workflow, enabling advanced capabilities such as image recognition, natural language processing, and decision-making.
IBM Robotics Platform
IBM offers a robust platform for robotics through its cloud services, focusing heavily on IoT device management and analytics. The integration of IBM’s Watson API provides powerful AI capabilities, allowing robots to process and analyze data effectively. IBM’s cloud services also offer extensive tools for managing and analyzing the data that robots collect, making it a strong contender in the AI-powered robotics space.

Innovations from Meta, NVIDIA, and Sereact
Beyond the major cloud providers, companies like Meta, NVIDIA, and Sereact are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with AI in robotics. Meta’s Ok Robot project (https://ok-robot.github.io/), NVIDIA’s Groot foundation model, and Sereact’s pickGPT (https://sereact.ai/pickgpt) all exemplify how generative AI is being used to enhance cognitive capabilities in robots. For instance, pickGPT is a multimodal large language model (LLM) designed for generalized robot manipulation, which demonstrates how LLMs can be applied to practical robotics tasks such as picking and sorting.
More details about how the multimodal LLM works: https://sereact.ai/posts/pickgpt-a-large-language-model-for-generalized-robot-manipulation

Figure 01
The robot Figure 01 received funding from major tech giants, including Amazon, Intel, NVIDIA, and Microsoft. One of its notable customers is BMW, which leverages Microsoft Azure for machine learning to enhance the robot’s capabilities.
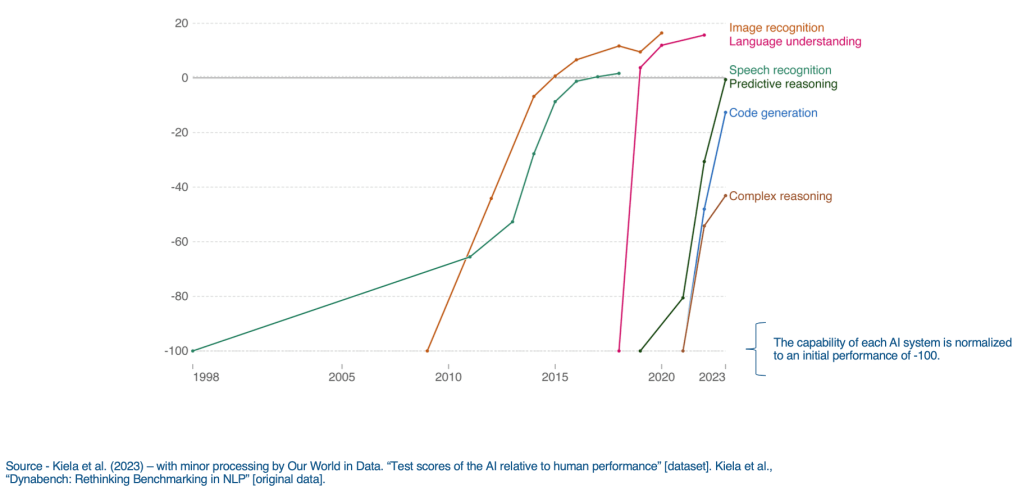
Machine cognitive capabilities measured against human (grey line)
Agility Robotics and Wayve: Pioneering New Frontiers
Agility Robotics and Wayve are also at the cutting edge of integrating AI into robotics. Agility Robotics utilizes LLMs to enhance the user interface for their robots, making interactions more intuitive. On the other hand, Wayve has developed a generative AI model named Gaia-1, which incorporates a world model to generate training scenarios for autonomous vehicles. Their Lingo-1 Vision-Language-Action-Model (VLAM) is particularly noteworthy as it can reason about autonomous driving and explain its decision-making process.

Conclusion
The integration of machine learning and generative AI into robotics is not just a trend but a transformative shift in how robots are developed, trained, and deployed. The insights shared by Dan Kara in the webinar underscore the collaborative efforts across various tech giants and innovative startups in pushing the envelope of what robots can achieve. As cloud services continue to evolve and AI models become more sophisticated, the future of robotics looks increasingly autonomous, intelligent, and interconnected.

Leave a comment